in this article we want to cover the different type of hosting. As you know the hosting company you use can dramatically affect your website’s performance, its uptime, and your overall experience and peace of mind. In this section, we will take you through our evaluation process and what we look for in a host.
There are many factors that go into our review process that we will discuss in more detail below. We take into account each hosting type, their allowed traffic levels, how much storage is provided (and its speed), the processing power of the CPUs, their uptime, quality of service, and their customer support. We individually test all of these factors to determine what the best web host is in each category. Our goal is to provide the best free and honest advice about web hosting we can.
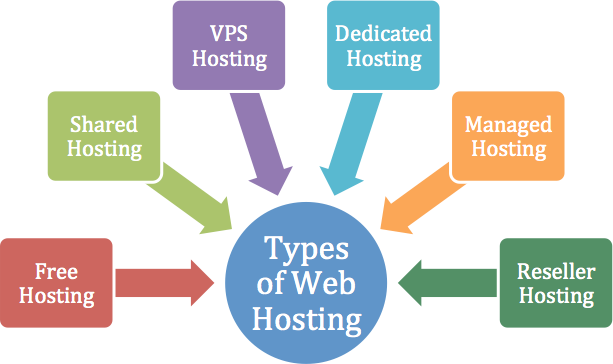
In the following sections, we will discuss each of the aforementioned factors in more detail and give you an idea of what we specifically look for when choosing a host. at bellow you can see the graphical reminder about type of hosting.
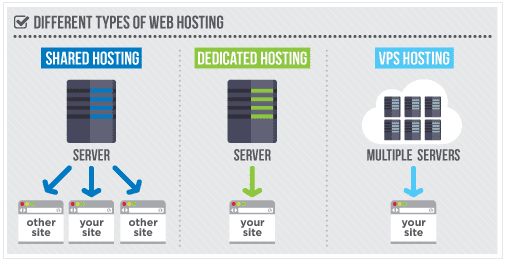
The type of hosting plays a large role in the evaluation of a web host. One host may have excellent shared hosting and terrible VPS hosting, or the other way around. Sometimes hosts focus on being great at something like WordPress hosting, but could care less about their shared hosting customers. We rate each hosting service by each of its hosting types individually, not in aggregate.
You’ll want to spend some time determining which type of hosting you’ll need for your site. Again, we highly recommend you read up on our types of Hosting section to help make that determination.
If you feel like you’re ready to go, great! We’ve done the leg work for you in determining the best hosting deals for each type of hosting.
The results…
- HostFeat Windows Shared Hosting
- HostFeat Dedicated Server Hosting
- HostFeat VPS Hosting
Bandwidth / Traffic
The bandwidth (or traffic) allowed by a web hosting plan refers to the amount of content sent from your server to a client’s browser. It’s a good idea to calculate the minimum bandwidth you’ll need before signing up for a hosting plan.
The Formula:
Visitors per Month x Page Size x Pages per Visit = Bandwidth Needed
Example:
Let’s say you have an average page size of 1MB. If your site gets 10,000 visitors per month and they average going to two pages each, then your bandwidth calculation goes like this:
10,000 Visits x 1MB Per Page x 2 Pages per Visit = 20GB of Bandwidth
Keep in mind, you’ll want to choose a plan that exceeds your minimum bandwidth needs just in case your traffic grows beyond its current levels.
Storage
As you Know Storage refers to the amount of content, data, and files you can store on your server.
Storage Size
Usually, websites do not have a tremendous amount of storage needs, but if you are hosting video or large images or user information, you may find this to be a concern. We do recommend having a minimum of 20 gigabytes (GB) of storage available for your web server.
Standard Hard Drives vs. SSD
Also, there are two different types of hard drives used these days. The standard hard drives are usually just referred to as say, “20GB Storage.” The other type of hard drive is referred to as an SSD, which stands for solid state drive. These drives are typically faster than standard hard drives and you may see them listed as “20GB SSD”.
Advanced Configurations and RAID
In addition, as you get to more and more complicated hosting, there are multiple options for hard drive configurations. These configurations have to do with making sure a single hard drive failure does not compromise your system and/or to increase the read and write speed of the drive.
As a brief introduction, there is a technology referred to as RAID (redundant array of inexpensive disks) that groups many hard drives into one logical drive. Below we have outlined some popular configurations you might see. Don’t worry if you don’t understand this. It makes very little difference for choosing a web host. We just want you to be aware of these terms in case you see them.
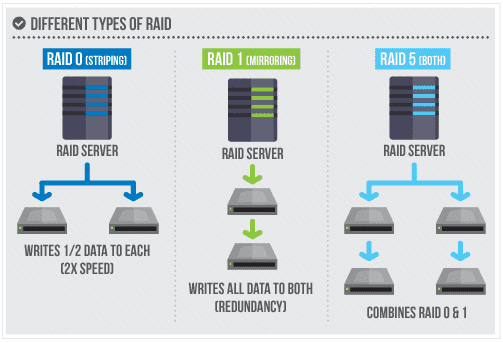
RAID 0
Uses two or more drives to parallelize writing to disks. This is called “striping.”
RAID 1
This is when two or more drives keep redundant copies of the data. Therefore, every write to one drive is also writing the data to the other. This is referred to as “mirroring.”
RAID 5
This is sort of a combination of RAID 0 and RAID 1. Three or more drives are basically used to both increase the write speed and mirror the drives. Usually, you’ll come across RAID 5 used in production.
There are other types of RAID available. We encourage you to research this further if you are interested.